Mastering future tenses in English is essential for clear and effective communication. Three common ways to discuss the future are “will,” “shall,” and “going to.” Each has distinct nuances and usage patterns, which we’ll explore in this comprehensive guide.
Understanding “Will”
“Will” is a versatile auxiliary verb used to express various types of future actions. Below are its primary uses:
- Expressing Decisions Made at the Moment of Speaking
- Example: I’ll call you after the meeting.
- Explanation: “Will” indicates a spontaneous decision.
- Making Predictions
- Example: It will rain tomorrow.
- Explanation: Predictions based on intuition or general knowledge often use “will.”
- Promises, Offers, and Threats
- Example: I’ll help you with your homework.
- Explanation: “Will” conveys commitments or intentions.
- Expressing Certainty
- Example: You’ll love this movie.
- Explanation: When speakers are confident about an outcome, “will” is appropriate.
Decoding “Shall”
“Shall” is less commonly used in modern English but remains relevant in specific contexts:
- Formal Suggestions and Offers
- Example: Shall we go for a walk?
- Explanation: “Shall” can be used for polite proposals.
- Legal or Formal Obligations
- Example: The tenant shall pay rent on the first of each month.
- Explanation: In legal or formal documents, “shall” denotes obligation.
- Expressing Determination (Old-Fashioned)
- Example: I shall overcome these challenges.
- Explanation: In literary or older texts, “shall” conveys resolve or intent.
Exploring “Going To”
“Going to” emphasizes plans, intentions, and evidence-based predictions:
- Planned Actions
- Example: I’m going to visit my grandparents next weekend.
- Explanation: Use “going to” for premeditated actions or decisions.
- Predictions Based on Evidence
- Example: Look at those clouds; it’s going to rain.
- Explanation: When there is visible evidence, “going to” is preferred.
- Informal Tone
- Example: I’m going to grab a coffee. Want one?
- Explanation: “Going to” suits casual conversation.
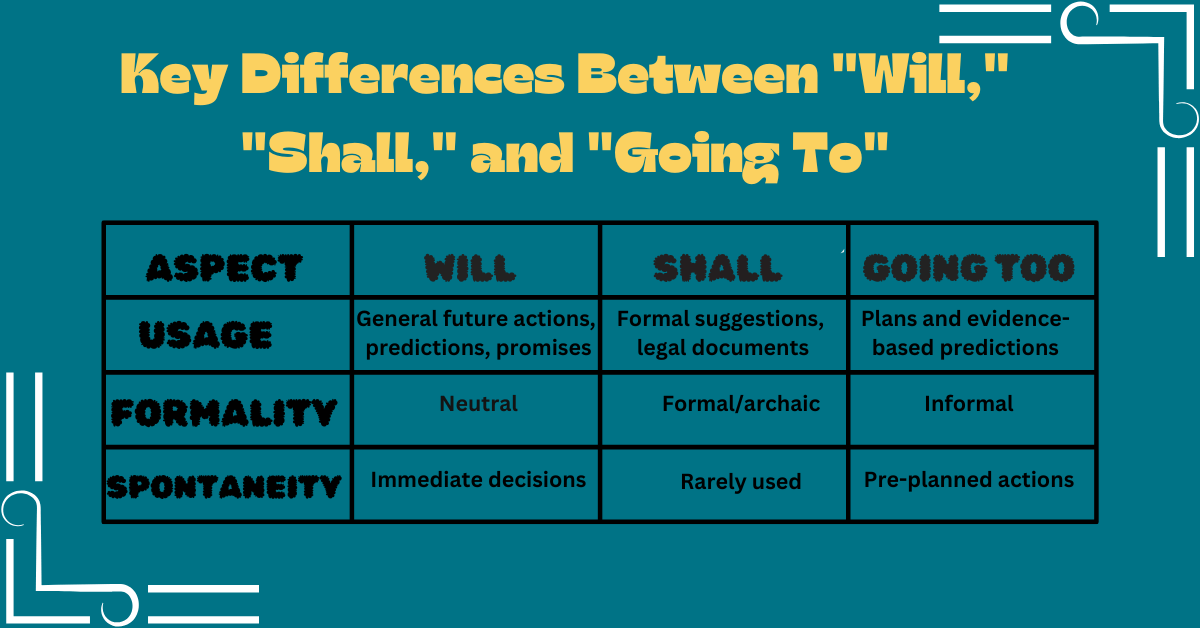
Key Differences Between “Will,” “Shall,” and “Going To”
| Aspect | Will | Shall | Going To |
|---|---|---|---|
| Usage | General future actions, predictions, promises | Formal suggestions, legal documents | Plans and evidence-based predictions |
| Formality | Neutral | Formal/archaic | Informal |
| Spontaneity | Immediate decisions | Rarely used | Pre-planned actions |
Tips for Choosing the Right Form
- Consider the context: Is it formal, casual, or spontaneous?
- Analyze the intent: Are you predicting, planning, or making an offer?
- Focus on regional preferences: British English tends to use “shall” more than American English.
Examples in Everyday Context
- Spontaneous Decisions: I’ll take care of it right away.
- Formal Suggestions: Shall we meet at 10 a.m.?
- Planned Actions: She’s going to study abroad next year.
- Predictions: It’s going to be a great day.
Conclusion
“Will,” “shall,” and “going to” each bring unique nuances to English communication. By understanding their specific roles and applications, you can confidently navigate future-tense expressions. Practice these distinctions in real-life scenarios to enhance your fluency and precision. Download the app for one on one spoken English practice with live English experts: https://engvarta.com