Have you ever paused mid-sentence because you weren’t sure if it’s “a umbrella” or “an umbrella”?
Or hesitated while texting someone because you didn’t know if it’s “a apple” or “an apple”?
Tiny words like A, An, and The may seem harmless — but they can seriously mess with your confidence if you don’t know how and when to use them.
And here’s the truth: even fluent English speakers sometimes second-guess these little words.
But not after today.
In this blog, we’ll break down the grammar behind A, An, The, share real-life examples (not boring ones), and even show you when you don’t need to use articles at all. No memorization. Just logic, sound, and some fun examples.
Oh — and there’s a short video waiting for you that brings it all to life 👇
Ready? Let’s go.
👉 If you’re just starting your English journey, this guide on the best English learning apps for beginners will help you get the right tools — and mastering A, An, The is a great place to begin.
Definite Article: “The”
“The” is called the definite article because it points to a specific thing that both the speaker and listener know about.
If you’re using “the”, you’re not talking about anything—you’re talking about that one particular thing.
Use “The” when:
- You’re referring to something unique or already mentioned
- There’s only one of something
- You and the listener both know what you’re talking about
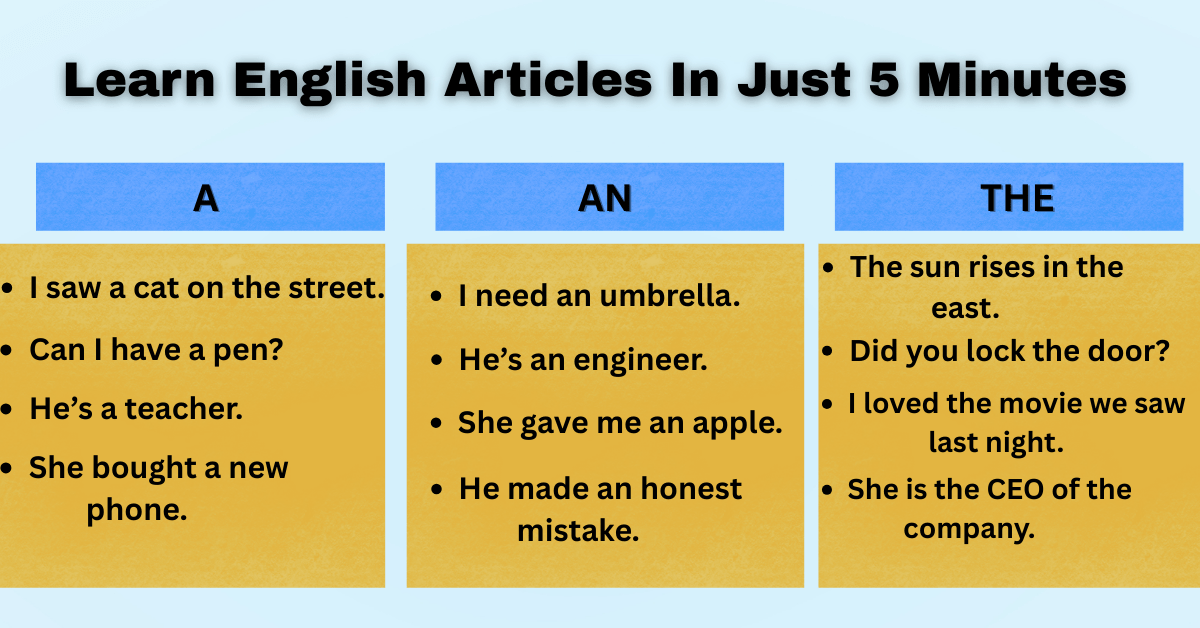
Real-Life Examples:
- “The sun rises in the east.”
→ There’s only one sun. It’s universal. So we say the sun. - “Did you lock the door?”
→ The person you’re talking to knows which door. It’s not just any door. - “I loved the movie we saw last night.”
→ You’ve already talked about this movie. It’s not a random one. - “She is the CEO of the company.”
→ There’s only one CEO. Only one company being referred to.
Bonus Tip:
Use “the” before:
- Superlative adjectives: the best, the tallest
- Musical instruments: the guitar, the piano
- Oceans, rivers, and deserts: the Ganga, the Himalayas, the Sahara
Indefinite Article: “A”
“A” is used when you’re talking about any one item, but you’re not being specific.
It’s like saying, “I don’t care which one, I just want one.”
Use “A” when:
- The next word starts with a consonant sound
- You’re introducing something non-specific
- The noun is countable and singular
Real-Life Examples:
- “I saw a cat on the street.”
→ Not a specific cat, just any cat. - “Can I have a pen?”
→ You’re not asking for a particular pen, just any one that works. - “He’s a teacher.”
→ One of many teachers in the world. Nothing specific. - “She bought a new phone.”
→ We don’t know which phone yet.
Indefinite Article: “An”
Just like “a”, “an” also means one, but not specific.
But the only difference?
It’s used before words that begin with a vowel sound (not just a vowel letter).
Use “An” when:
The next word starts with a vowel sound (a, e, i, o, u)
The noun is non-specific, singular, and countable
Real-Life Examples:
- “I need an umbrella.”
→ ‘Umbrella’ begins with a vowel sound: uhm-brella - “He’s an engineer.”
→ Begins with a vowel sound: en-jineer - “She gave me an apple.”
→ Not a specific apple. Just one. - “He made an honest mistake.”
→ Honest starts with a silent “h”, so the sound is on-est → vowel sound.
Quick Trick:
It’s about the sound, not the letter.
So you say:
- an hour (silent “h” → vowel sound)
- a university (“you-niversity” → starts with a consonant sound)
Omission of Articles (When NOT to Use A, An, The)
Sometimes, no article is needed at all — especially when speaking generally.
Don’t use articles with:
- Plural or uncountable nouns (general idea)
“Cats are cute.”
“Milk is healthy.”
- Names of people, places, companies
“Akash is my friend.”
“I visited India last year.”
“Google is a big company.”
- Meals and time expressions
“She eats lunch at noon.”
“We’ll meet after dinner.”
- Languages and subjects
“He speaks English.”
“Math is hard.”
Understanding the use of articles in English grammar is essential for clear and effective communication. “The” points to something specific, while “a” and “an” introduce non-specific nouns. By mastering the usage of these articles, you can enhance the precision and clarity of your English writing and conversation. Practice and exposure to the language will help you become more proficient in using articles correctly.
Confused about articles? This video will fix that in 2 minutes
In this quick video, you’ll learn:
What will you learn in this video?
1️⃣ What A, An, and The really mean
2️⃣ How to use the definite article “The”
3️⃣ When to use “A”, “An”, “The” (and when not to)
4️⃣ The one trick that makes choosing between ‘a’ and ‘an’ super easy
5️⃣ Plenty of real-life examples to ensure you get it
👉 Watch it now and never get stuck again.
Articles might be tiny, but they’re powerful.
Mastering them isn’t about memorizing a list of rules; it’s about hearing the rhythm of English and flowing with it.
Now that you know when to use A, An, and The, you’ll start noticing them everywhere. And when you use them correctly, you’ll sound more fluent, more confident, and more natural.
But don’t stop at reading.
Want to practice using A, An, The in real conversations — with real people?
On EngVarta, you can speak with live English experts who’ll gently correct your mistakes and help you gain fluency, one session at a time.
Practice grammar, pronunciation, and fluency in real time.
Download the EngVarta app and start speaking today.
Because your English deserves more than just theory — it deserves a voice.